 GATB
GATB
GATB (Graphical Articulated Total Body)
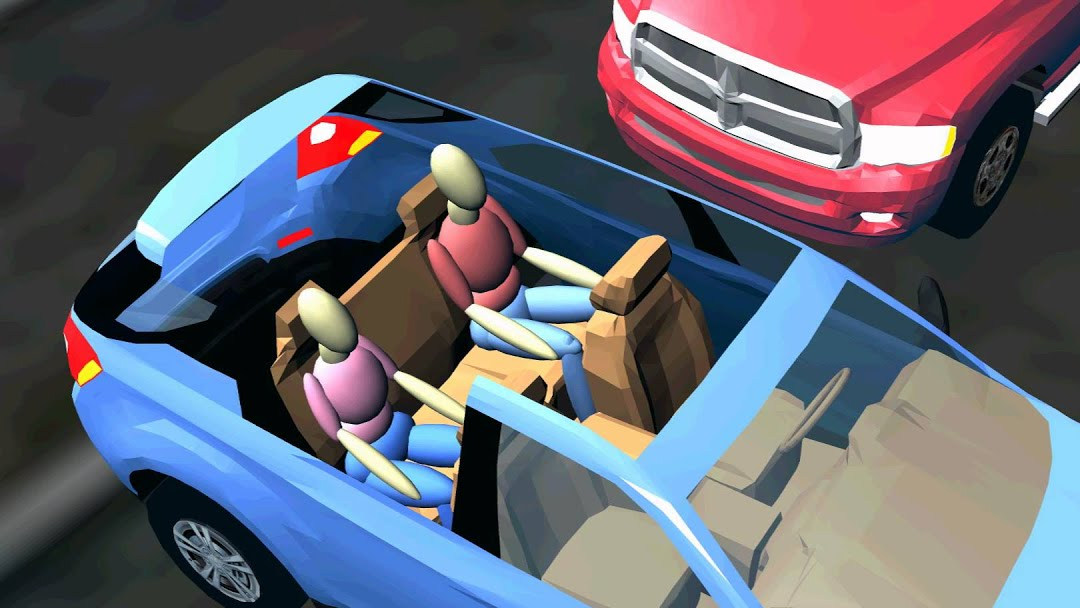
GATB is a detailed computer model of the human body, representing the human body with 15-segments and 14-joints. The GATB model has 48 degrees-of-freedom for each human. Each of the 15 mass segments can move and interact with the environment.
Using GATB, a human model can be placed inside a car during a crash to predict how the human would move, what they would hit inside the car, or how an ejection could occur. GATB can also be used to simulate a human body being struck by a vehicle's exterior to study pedestrian impacts. Adults and children can be modeled using actual heights and weights so that specific crashes can be studied to determine how injuries occurred. Test dummies can also be modeled using GATB. Car manufacturers can use GATB to study a crash test on the computer prior to crashing real vehicles. This allows researchers to explore proposed test configurations to ensure the test is performed properly.
GATB helps determine the speeds and forces that people experience during a collision. Safety researchers can use this information to study how injuries occur, and design safer vehicles and roads.
GATB is an HVE-compatible version of the widely used ATB computer program first developed by Calspan and enhanced by the US Air Force. The GATB program is further described in SAE Paper 970967, "Using ATB Under the HVE Environment".
GATB was previously available from Collision Engineering Associates, Inc.

